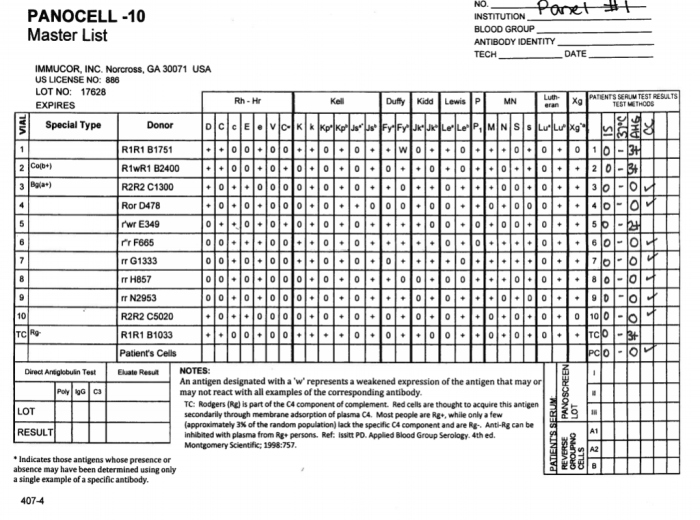
Antibody Panel Practice with Answers is an authoritative guide that provides a comprehensive overview of current antibody panel practices in healthcare. This invaluable resource offers a deep dive into the different types of antibody panels available, their advantages and disadvantages, and their applications in diagnosing and monitoring diseases.
Throughout this meticulously crafted narrative, readers will gain a profound understanding of antibody panel interpretation, including the factors that can influence results. The guide also explores the various ways antibody panel results can be reported and communicated effectively to patients and healthcare providers, emphasizing the significance of clear and accurate reporting.
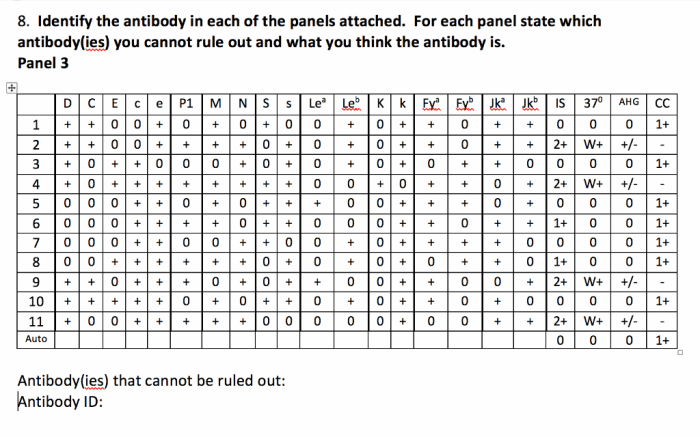
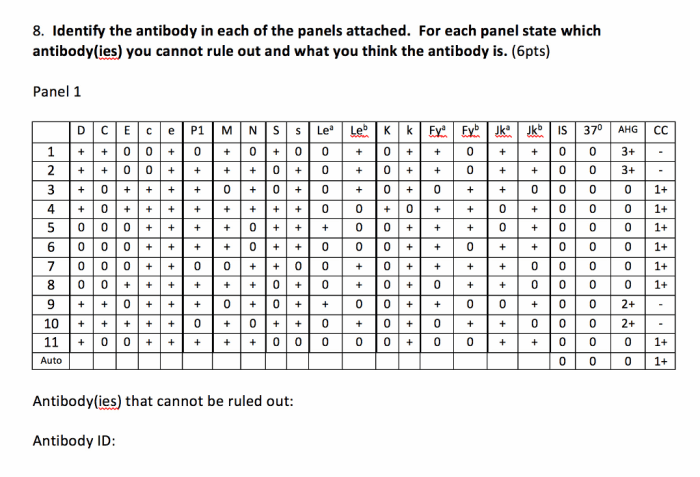
Antibody Panel Practices
Antibody panels are an essential tool in the diagnosis and management of various immunological disorders. They are a collection of tests that measure the levels of different antibodies in the blood, providing valuable insights into the immune system’s response to specific antigens.
Antibody panels are used in a wide range of clinical settings, including the diagnosis of autoimmune diseases, infectious diseases, and allergies. They can also be used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and to identify individuals at risk of developing certain diseases.
Types of Antibody Panels
There are several different types of antibody panels available, each designed to detect a specific set of antibodies. The most common types of antibody panels include:
- Autoimmune antibody panels: These panels test for antibodies that are directed against the body’s own tissues. They are used to diagnose autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and celiac disease.
- Infectious disease antibody panels: These panels test for antibodies that are directed against specific infectious agents, such as viruses, bacteria, and parasites. They are used to diagnose and monitor infectious diseases such as HIV, hepatitis, and Lyme disease.
- Allergy antibody panels: These panels test for antibodies that are directed against specific allergens, such as pollen, dust mites, and pet dander. They are used to diagnose and manage allergies.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Antibody Panels
Antibody panels offer several advantages over other diagnostic tests. They are relatively inexpensive, easy to perform, and can provide a wealth of information about the immune system. However, there are also some disadvantages to using antibody panels.
- False positives and false negatives: Antibody panels can sometimes produce false positive or false negative results. This can be due to a variety of factors, such as the presence of interfering antibodies or the timing of the test.
- Limited sensitivity: Antibody panels may not be able to detect all antibodies that are present in the blood. This can make it difficult to diagnose certain diseases, especially in the early stages.
- Interpretation challenges: Interpreting antibody panel results can be challenging, especially for non-specialists. This is because the levels of antibodies can vary widely depending on the individual’s age, sex, and health status.
Despite these limitations, antibody panels remain a valuable tool in the diagnosis and management of immunological disorders. They provide a wealth of information about the immune system and can help to guide treatment decisions.
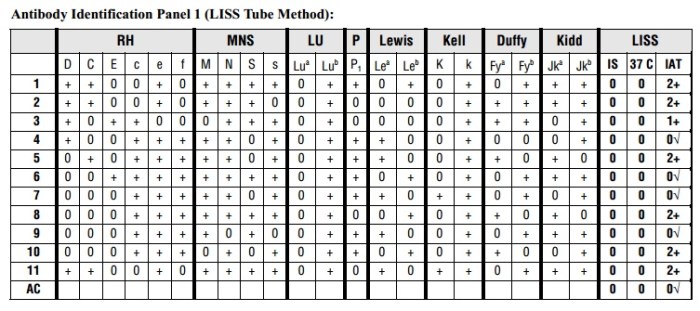
Antibody Panel Interpretation
Antibody panels are used to detect the presence of antibodies in a patient’s serum. These antibodies can be produced in response to infection, vaccination, or autoimmune diseases. The interpretation of antibody panels can be complex, and a number of factors can affect the results.
Factors Affecting Antibody Panel Interpretation
- The type of antibody panel used:Different antibody panels test for different antibodies. Some panels are more comprehensive than others, and some are designed to detect specific types of antibodies.
- The timing of the test:The timing of the test can affect the results. Antibodies may not be detectable until several days or weeks after an infection. In some cases, antibodies may persist for months or even years after an infection.
- The patient’s immune status:The patient’s immune status can affect the results of an antibody panel. Patients with weakened immune systems may not produce antibodies in response to infection.
- The presence of other medical conditions:The presence of other medical conditions can affect the results of an antibody panel. For example, patients with autoimmune diseases may have antibodies that react against their own tissues.
Uses of Antibody Panels
Antibody panels can be used to diagnose and monitor a variety of diseases. Some of the most common uses of antibody panels include:
- Diagnosis of infectious diseases:Antibody panels can be used to diagnose a variety of infectious diseases, including measles, mumps, rubella, and HIV.
- Monitoring of vaccine immunity:Antibody panels can be used to monitor vaccine immunity. This can help to ensure that patients are protected against specific diseases.
- Diagnosis of autoimmune diseases:Antibody panels can be used to diagnose autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and multiple sclerosis.
- Monitoring of treatment:Antibody panels can be used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment for infectious diseases and autoimmune diseases.
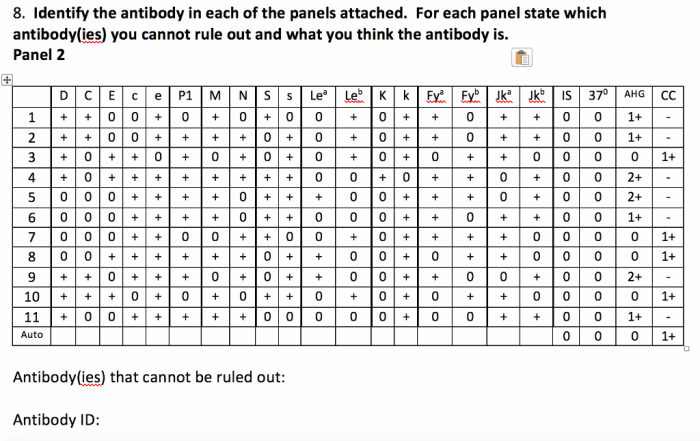
Antibody Panel Reporting
Antibody panel results can be reported in various formats, depending on the laboratory and the specific antibodies being tested. Some common reporting methods include:
- Narrative report:This type of report provides a written description of the antibody results, including the specific antibodies tested, the results of each test, and any relevant interpretations or comments.
- Table format:This type of report presents the antibody results in a tabular format, with each antibody listed in a separate row and the results displayed in the corresponding columns. This format allows for easy comparison of the results for different antibodies.
- Graphical format:This type of report presents the antibody results in a graphical format, such as a bar graph or scatter plot. This format can be useful for visualizing the distribution of the results and identifying any trends or patterns.
Antibody panel results can be used to communicate with patients and other healthcare providers in a variety of ways. For example, they can be used to:
- Diagnose autoimmune diseases:Antibody panels can help to diagnose autoimmune diseases by detecting the presence of specific antibodies that are associated with these diseases.
- Monitor disease activity:Antibody panels can be used to monitor the activity of autoimmune diseases by tracking the levels of specific antibodies over time.
- Guide treatment decisions:Antibody panel results can be used to guide treatment decisions by providing information about the specific antibodies that are involved in a patient’s disease.
Clear and accurate antibody panel reporting is essential for ensuring that the results are interpreted correctly and used appropriately. This includes providing complete and accurate information about the antibodies being tested, the results of each test, and any relevant interpretations or comments.
It is also important to use clear and concise language that is easy for patients and other healthcare providers to understand.
Antibody Panel Quality Assurance
Quality assurance (QA) is of paramount importance in antibody panel testing to ensure the accuracy, reliability, and consistency of the results. Effective QA measures help minimize errors, improve patient safety, and maintain the integrity of the laboratory process.
Internal Controls
- Positive and negative controls are included in each test run to verify the performance of the reagents and equipment.
- Calibration and verification procedures are performed regularly to ensure the accuracy of the instruments.
- External proficiency testing programs are used to compare laboratory results with those of other laboratories.
External Controls
- Regularly participating in external proficiency testing programs ensures the laboratory’s performance meets established standards.
- External audits by regulatory agencies or accreditation bodies assess the laboratory’s compliance with quality standards.
Documentation and Training
- Proper documentation of all QA procedures and results is essential for traceability and accountability.
- Ongoing training for laboratory personnel ensures they are up-to-date on the latest techniques and quality standards.
Examples of QA Improvements, Antibody panel practice with answers
- Implementation of QA measures has led to a significant reduction in false-positive and false-negative results in antibody panel testing.
- External proficiency testing programs have identified areas for improvement, resulting in enhanced accuracy and reliability.
- Regular training has improved the skills and knowledge of laboratory personnel, contributing to the overall quality of the testing process.
Expert Answers: Antibody Panel Practice With Answers
What are the different types of antibody panels available?
Antibody panels vary in their composition, targeting different antigens or groups of antigens. Some common types include viral antibody panels, bacterial antibody panels, and autoimmune antibody panels.
How are antibody panel results interpreted?
Antibody panel results are interpreted based on the presence or absence of specific antibodies and their titers (concentrations). Positive results indicate the presence of antibodies against a particular antigen, while negative results indicate their absence.
What are the advantages of using antibody panels?
Antibody panels offer several advantages, including their ability to detect multiple antibodies simultaneously, providing a broader view of an individual’s immune response. They can also aid in the diagnosis of complex diseases and monitor disease progression and treatment response.