Atomic structure word search answer key uncovers the fundamental building blocks of matter, guiding us on an enlightening journey into the microscopic realm of atoms. This comprehensive resource provides a detailed exploration of atomic structure, revealing the intricate relationships between protons, neutrons, and electrons that define the very essence of elements.
Delving into the intricacies of atomic structure, we unravel the mysteries of electron configurations, periodic trends, and chemical bonding. By understanding the arrangement of electrons within energy levels and the periodic patterns that govern atomic properties, we gain invaluable insights into the behavior of elements and their interactions with one another.
Atomic Structure Basics: Atomic Structure Word Search Answer Key
Atoms are the fundamental building blocks of matter. They are composed of three subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons reside in the nucleus of the atom, while electrons orbit around the nucleus in specific energy levels.
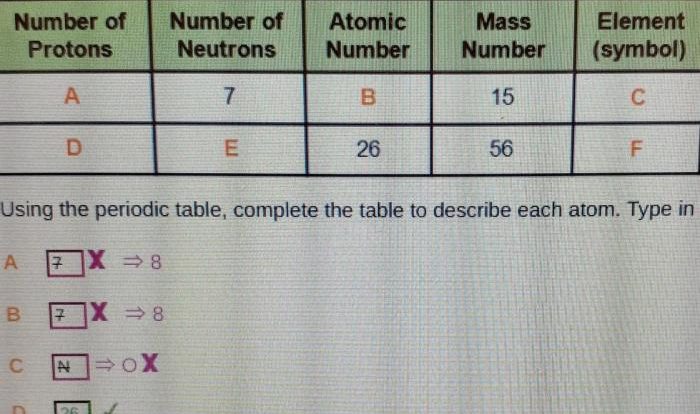
The atomic number of an element is the number of protons in its nucleus. This number uniquely identifies the element and determines its position on the periodic table. The mass number of an element is the total number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus.

Electron Configuration
Electrons are arranged within energy levels or shells around the nucleus. Each shell can hold a specific number of electrons: the first shell can hold up to 2 electrons, the second shell can hold up to 8 electrons, and so on.
The Aufbau principle states that electrons fill the lowest energy levels first. Hund’s rule states that electrons in the same subshell will occupy different orbitals with parallel spins before pairing up.
- Hydrogen: 1s 1
- Helium: 1s 2
- Lithium: 1s 22s 1
- Carbon: 1s 22s 22p 2
- Nitrogen: 1s 22s 22p 3
Periodic Trends, Atomic structure word search answer key
Atomic structure exhibits periodic trends across the periodic table. These trends include:
- Atomic radius: The atomic radius generally increases down a group and decreases across a period.
- Ionization energy: The ionization energy generally increases across a period and decreases down a group.
- Electronegativity: The electronegativity generally increases across a period and decreases down a group.
These trends can be explained by the increasing nuclear charge and the shielding effect of inner electrons.
Chemical Bonding
Atomic structure plays a crucial role in determining the type of chemical bond that can form between atoms. There are three main types of chemical bonds:
- Covalent bonds: Formed by the sharing of electrons between atoms.
- Ionic bonds: Formed by the transfer of electrons from one atom to another.
- Metallic bonds: Formed by the sharing of electrons in a sea of delocalized electrons.
The type of bond formed depends on the electronegativity difference between the atoms involved.
Applications of Atomic Structure
Atomic structure has wide-ranging applications in various fields, including:
- Chemistry: Understanding atomic structure is essential for predicting and explaining chemical reactions.
- Materials science: The properties of materials can be tailored by manipulating their atomic structure.
- Nanotechnology: Atomic structure is crucial for the design and fabrication of nanomaterials.
By understanding atomic structure, scientists can gain insights into the behavior of matter and develop new technologies.
Commonly Asked Questions
What is the atomic structure?
Atomic structure refers to the arrangement of protons, neutrons, and electrons within an atom, defining the fundamental properties and behavior of an element.
What is the significance of electron configuration?
Electron configuration describes the distribution of electrons across energy levels, influencing chemical bonding, reactivity, and other atomic properties.
How does atomic structure impact chemical bonding?
Atomic structure determines the number and arrangement of valence electrons, which play a crucial role in forming chemical bonds between atoms.