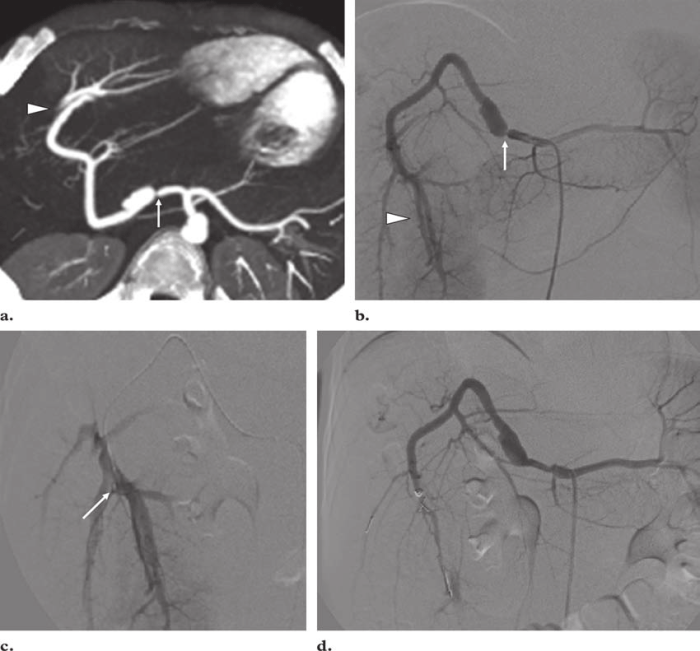
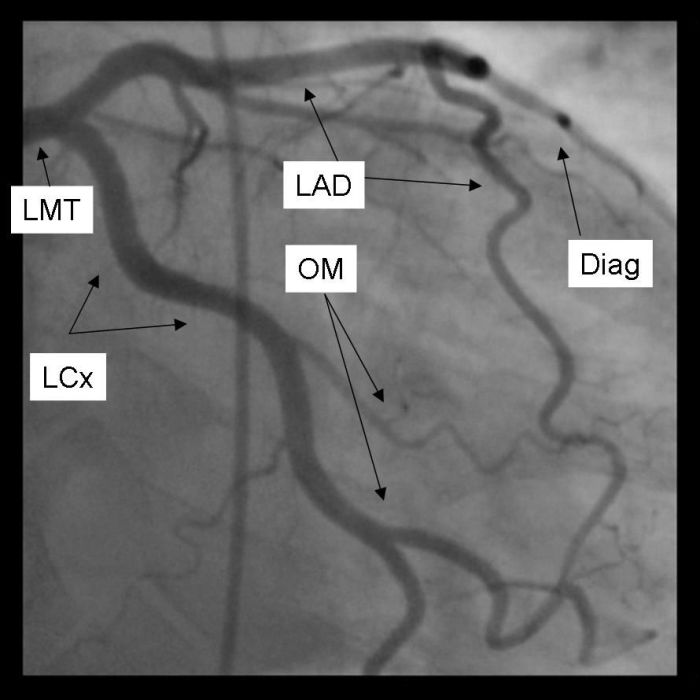
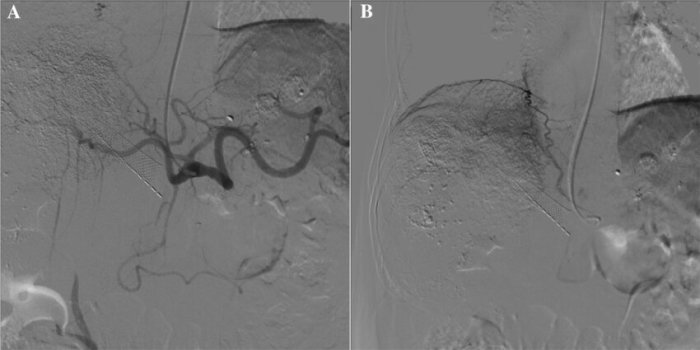
Percutaneous carotid catheterization and arteriogram were performed – Percutaneous carotid catheterization and arteriogram, a minimally invasive procedure, provides invaluable insights into the health of carotid arteries, enabling timely diagnosis and effective treatment of carotid artery disease. This procedure involves threading a thin catheter through the femoral artery and into the carotid arteries, allowing for the injection of contrast dye and subsequent imaging to assess the arteries’ condition.
The indications for percutaneous carotid catheterization and arteriogram include evaluating carotid artery stenosis, a narrowing of the arteries, as well as diagnosing and monitoring conditions such as carotid artery dissection and aneurysms. The procedure is also crucial in guiding treatment decisions, including carotid endarterectomy and stenting.
Percutaneous Carotid Catheterization and Arteriogram: Percutaneous Carotid Catheterization And Arteriogram Were Performed
Percutaneous carotid catheterization and arteriogram is a minimally invasive procedure used to visualize the carotid arteries, which supply blood to the brain. It involves inserting a thin, flexible catheter into the carotid artery and injecting a contrast agent to make the arteries visible on X-ray images.
The purpose of the procedure is to evaluate the carotid arteries for narrowing or blockages, which can increase the risk of stroke. It is typically performed in patients who have symptoms of carotid artery disease, such as transient ischemic attacks (TIAs) or a history of stroke.
Technique
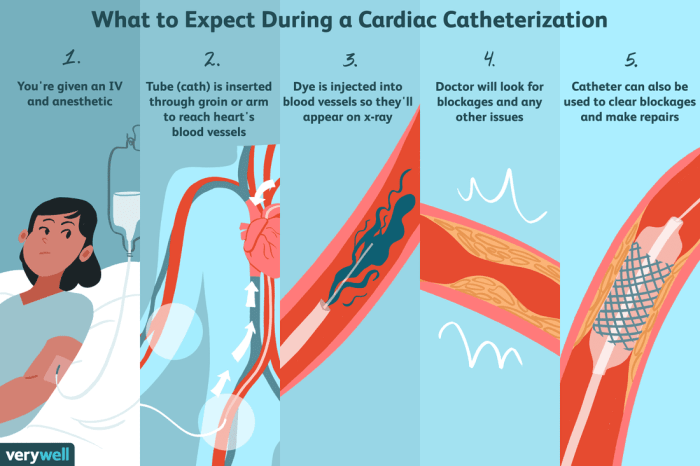
Percutaneous carotid catheterization and arteriogram is performed by an interventional radiologist or vascular surgeon. The procedure typically takes about 30 minutes to complete.
- The patient lies on their back on an X-ray table.
- The neck is shaved and cleaned.
- A local anesthetic is injected into the skin at the puncture site.
- A small incision is made in the skin and the carotid artery is accessed using a needle.
- A guidewire is inserted into the artery and advanced into the carotid artery.
- The catheter is inserted over the guidewire and advanced into the carotid artery.
- Contrast agent is injected into the carotid artery and X-ray images are taken.
- The catheter is removed and the puncture site is closed with a small bandage.
Imaging techniques used during the procedure include fluoroscopy and digital subtraction angiography (DSA). Fluoroscopy is a real-time X-ray imaging technique that allows the doctor to visualize the catheter and contrast agent as they move through the carotid artery. DSA is a type of X-ray imaging that removes the bones from the images, making the arteries more visible.
Potential complications of the procedure include bleeding, infection, and damage to the carotid artery. However, these complications are rare.
Interpretation of Results
The results of the procedure are interpreted by a radiologist. The radiologist will look for any narrowing or blockages in the carotid arteries.
Normal findings on a carotid arteriogram include smooth, open arteries with no narrowing or blockages.
Abnormal findings that may be seen on a carotid arteriogram include:
- Narrowing of the carotid artery (stenosis)
- Blockage of the carotid artery (occlusion)
- Aneurysm (a ballooning of the carotid artery)
- Dissection (a tear in the wall of the carotid artery)
Clinical Applications, Percutaneous carotid catheterization and arteriogram were performed
Percutaneous carotid catheterization and arteriogram is used to diagnose and treat carotid artery disease. The procedure can be used to:
- Confirm the diagnosis of carotid artery disease
- Determine the severity of carotid artery disease
- Guide treatment decisions, such as whether to perform carotid endarterectomy (CEA) or carotid artery stenting (CAS)
- Monitor the results of CEA or CAS
The procedure has been shown to improve patient outcomes by reducing the risk of stroke in patients with carotid artery disease.
Helpful Answers
What is the purpose of percutaneous carotid catheterization and arteriogram?
Percutaneous carotid catheterization and arteriogram provide detailed images of the carotid arteries to assess their health, diagnose conditions such as carotid artery stenosis, and guide treatment decisions.
How is percutaneous carotid catheterization and arteriogram performed?
A thin catheter is inserted into the femoral artery and guided through the arteries to the carotid arteries. Contrast dye is injected, and X-ray images are taken to visualize the arteries.
What are the potential risks of percutaneous carotid catheterization and arteriogram?
Potential risks include bleeding, infection, and damage to the carotid arteries. However, these risks are generally low when the procedure is performed by an experienced physician.