Dive into the fascinating world of breeding bunnies in a lab setting with our comprehensive guide, breeding bunnies lab answer key. This in-depth resource provides a captivating overview of the topic, exploring the ethical considerations, scientific applications, and practical techniques involved in this specialized field.
From understanding the methods used for breeding bunnies to ensuring their proper care and management, this guide covers every aspect of this intriguing subject.
Breeding Bunnies Lab
Breeding bunnies in a laboratory setting is a common practice in scientific research. It allows scientists to control the genetic and environmental factors of the animals, making it easier to study specific traits and behaviors.
There are several ethical considerations involved in breeding animals in captivity. One concern is the welfare of the animals. It is important to ensure that the bunnies are provided with a comfortable and healthy environment, including adequate food, water, and space to move around.
Contribution to Scientific Research
Breeding bunnies in a lab can contribute to scientific research in several ways. One example is the study of genetics. By breeding bunnies with specific genetic traits, scientists can learn more about how genes are inherited and how they affect the development and behavior of the animals.
Another example is the study of nutrition. By feeding bunnies different diets, scientists can learn more about the effects of diet on the health and development of the animals.
Breeding bunnies in a lab can also help scientists to develop new drugs and treatments for diseases. By studying the effects of different drugs on the bunnies, scientists can learn more about how these drugs work and how they can be used to treat diseases in humans.
Methods for Breeding Bunnies

Breeding bunnies in a lab setting requires careful planning and execution to ensure the health and well-being of the animals. Several methods are commonly used for breeding bunnies in a lab, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
One of the most common methods is natural mating, where a male and female bunny are introduced to each other in a controlled environment. This method allows the bunnies to mate naturally, and it is often successful in producing offspring.
Breeding bunnies in a lab setting requires careful planning and execution. However, if you’re curious about the safety of resin canals in mangoes, you can check out this article: resin canal mango safe to eat . It’s important to note that while this information is helpful, it doesn’t replace the need for proper breeding techniques when working with bunnies in a lab environment.
However, natural mating can be unpredictable, and it may not always result in pregnancy.
Another method is artificial insemination (AI), where sperm is collected from a male bunny and artificially introduced into the female’s reproductive tract. AI is a more controlled method of breeding, and it can be used to improve the genetic diversity of a breeding program.
However, AI requires specialized equipment and training, and it can be more expensive than natural mating.
Embryo transfer is a more advanced method of breeding bunnies, where embryos are collected from a female bunny and implanted into the uterus of a surrogate mother. This method allows for the production of multiple offspring from a single female, and it can be used to improve the genetic diversity of a breeding program.
However, embryo transfer is a complex and expensive procedure, and it requires specialized equipment and training.
Regardless of the method used, it is important to maintain genetic diversity in breeding programs to avoid inbreeding and the associated health problems. This can be achieved by using multiple breeding pairs, introducing new animals into the breeding program, and avoiding breeding closely related individuals.
Step-by-Step Guide to Breeding Bunnies in a Lab Setting, Breeding bunnies lab answer key
- Obtain healthy breeding pairs of bunnies.
- Provide a clean and comfortable environment for the bunnies.
- Monitor the bunnies for signs of heat (estrus) in females and readiness to mate in males.
- Introduce the male and female bunnies to each other in a controlled environment.
- Allow the bunnies to mate naturally.
- Monitor the female bunny for signs of pregnancy.
- Provide a nesting box for the female bunny to give birth in.
- Care for the newborn bunnies and their mother.
Care and Management of Breeding Bunnies: Breeding Bunnies Lab Answer Key
Breeding bunnies require specific care and management practices to ensure their health, well-being, and reproductive success. Proper care includes providing appropriate nutrition, maintaining a clean and stimulating environment, and offering enrichment activities to promote physical and mental health.
Nutritional Needs
Breeding bunnies have higher nutritional demands compared to non-breeding rabbits. A well-balanced diet is essential for optimal reproductive performance, fetal development, and milk production. The table below Artikels the nutritional needs of breeding bunnies:
| Nutrient | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Protein | 16-18% |
| Fat | 3-5% |
| Fiber | 18-20% |
| Calcium | 1% |
| Phosphorus | 0.75% |
| Vitamin A | 10,000 IU/kg |
| Vitamin D | 2,000 IU/kg |
Enrichment Activities
Enrichment activities are crucial for the well-being of breeding bunnies. These activities provide mental and physical stimulation, reducing boredom and promoting natural behaviors. Suitable enrichment activities include:
- Providing toys such as cardboard boxes, tunnels, and chew blocks
- Offering fresh vegetables and herbs for foraging
- Creating hiding places and elevated platforms for exploration
- Introducing social interaction with other rabbits under supervision
Regular monitoring and observation of breeding bunnies are essential to ensure their health and detect any potential problems. A clean and comfortable environment, proper nutrition, and enrichment activities are key factors in maintaining the health and reproductive success of breeding bunnies in a lab setting.
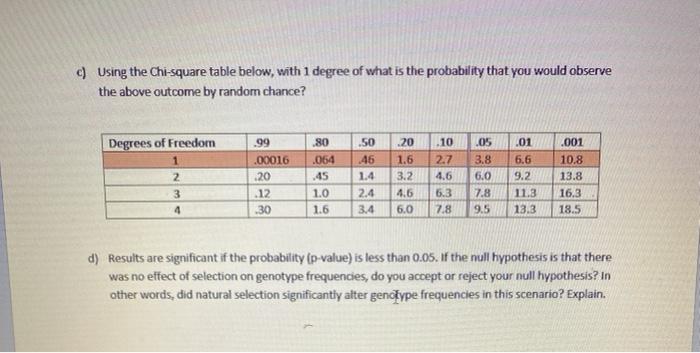
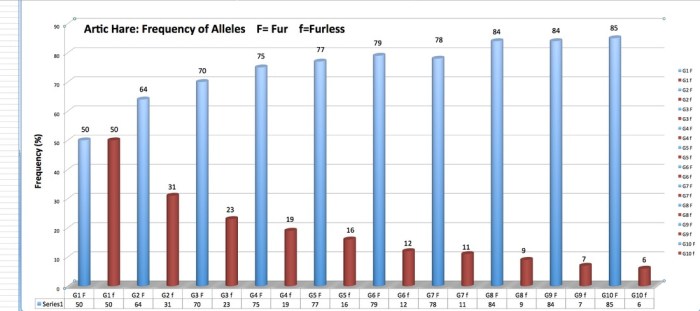
Monitoring and Data Collection
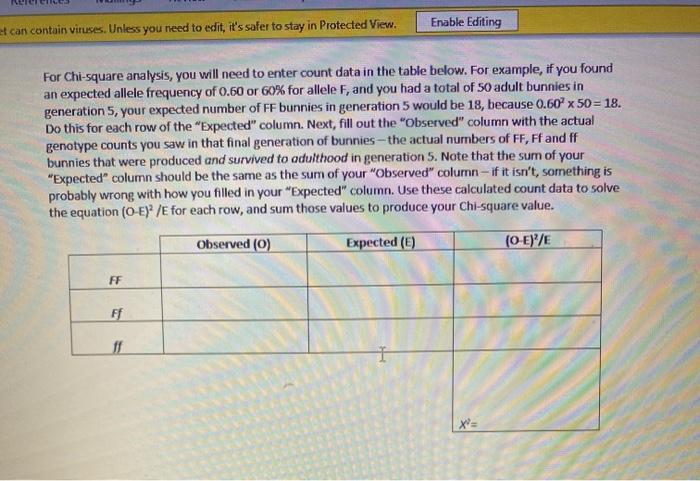
Effective breeding programs rely heavily on monitoring the health and progress of breeding bunnies. This involves regular checkups, observing their behavior, and tracking their breeding data. Maintaining accurate records is crucial for evaluating the success of the breeding program, identifying potential issues, and making informed decisions.
Methods for Monitoring Health and Progress
- Regular Checkups:Breeders should conduct routine physical examinations to assess the overall health of the bunnies, including their weight, body condition, and any signs of illness or injury.
- Behavioral Observations:Monitoring the behavior of breeding bunnies provides valuable insights into their well-being and reproductive status. Observing their interactions, feeding habits, and nesting behavior can help identify potential problems early on.
- Litter Monitoring:Tracking the size, weight, and survival rate of litters helps assess the fertility and productivity of breeding bunnies. It also provides information about the genetic traits and potential health issues within the colony.
Importance of Accurate Record Keeping
Maintaining accurate breeding records is essential for several reasons:
- Tracking Breeding Progress:Records allow breeders to track the breeding history of each bunny, including the dates of mating, litter sizes, and any health issues encountered.
- Evaluating Breeding Success:By analyzing breeding data, breeders can assess the effectiveness of their breeding program and identify areas for improvement.
- Identifying Potential Issues:Regular monitoring and record keeping help breeders identify potential problems early on, such as low fertility rates, high mortality rates, or genetic defects.
Sample Data Collection Form
Below is a sample data collection form that breeders can use to track the breeding progress of their bunnies:
| Bunny ID | Date of Mating | Litter Size | Litter Weight | Survival Rate | Health Observations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B001 | 2023-03-05 | 8 | 120g | 100% | Healthy and active |
| B002 | 2023-03-12 | 6 | 90g | 80% | One stillborn |
FAQ Compilation
What are the ethical considerations involved in breeding animals in captivity?
Breeding animals in captivity raises important ethical questions regarding their welfare, genetic diversity, and the potential impact on wild populations.
How do breeding bunnies contribute to scientific research?
Breeding bunnies in a lab setting allows researchers to study various aspects of reproduction, genetics, and disease models, contributing to advancements in biomedical research.
What are the key steps involved in breeding bunnies in a lab?
Breeding bunnies in a lab requires careful planning, including selecting suitable breeding pairs, providing proper housing and nutrition, and monitoring their health and progress.
